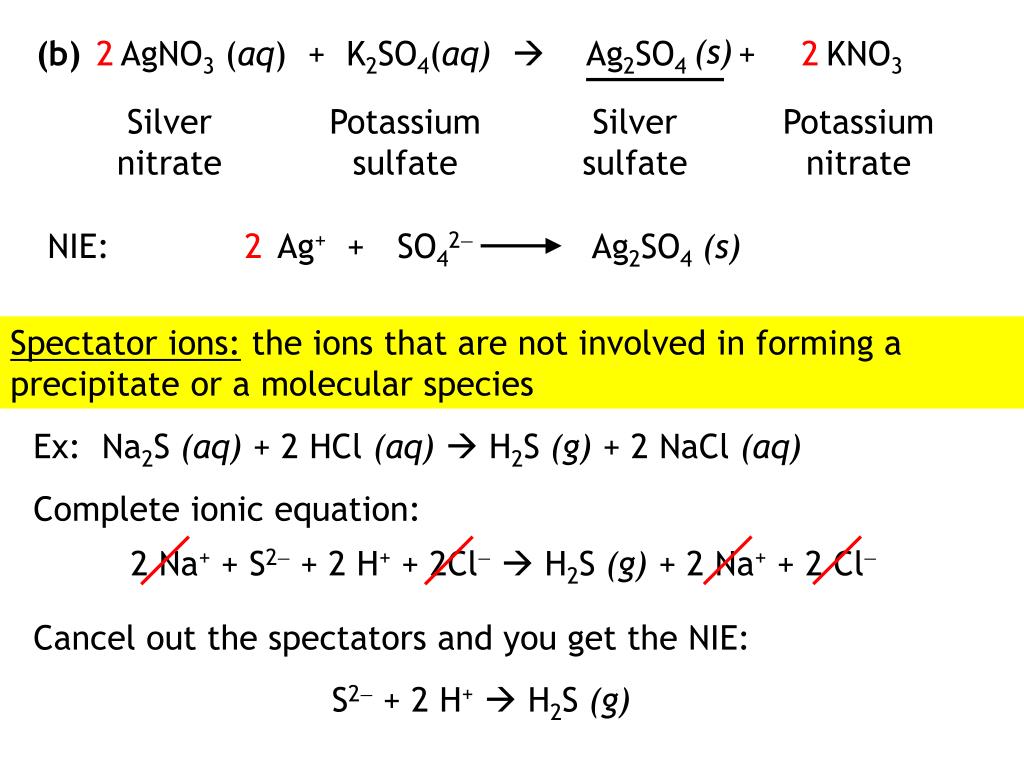
Question: (aq) + (aq) + 1. Al2(SO4)3 (aq) → 2. (NH4)2CO3 (aq) → 3. LizCrO4 (aq) → 4. Sn(ClO4)4 (aq) → (aq) (aq) (aq)) (aq) (aq) + (aq) +.Spectator ions: NH41+ (aq) and SO42- (aq).19. Balanced equations for precipitation reactions: (a) NiCl2(aq) + (NH4)2S(aq) → NiS(s) + 2 NH4Cl(aq) Net ionic equation: Ni2+(aq) + S2-(aq) → NiS(s). H2SO4 is an acid, and Zn(OH)2 acts as a base. (c) Oxidation-Reduction: Ca(s) has 3. Each CO2 provides the O atom for a molecule of H2O.This is due to the acidic nature of sf(Cr_((aq))^(3+)). The hydrogen ions react with the carbonate ions in an acid/base reaction: sf(2H_3O^(+)+CO_(3)^(2-)rarr3H_2O+CO_2) Effervescence is observed due to the formation of sf(CO_2).2.5 Взаимодействие нитрата или хлорида хрома(III) и сульфата аммония. Дигидрофосфат аммония (NH4H2PO4) • Дихромат аммония ((NH4)2Cr2O7) • Нитрат аммония (NH4NO3) • Перренат аммония (NH4ReO4) • Сульфат аммония ((NH4)2SO4) • Сукцинат аммония ((NH4)...
Write the balanced net ionic equation for the reaction... | Yahoo Answers
(NH4)2CO3(aq). Always use the upper case for the first character in the element name and the lower case for the second character. Examples: Fe, Au, Co, Br, C, O, N, F. Compare: Co - cobalt and CO - carbon monoxide.The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula NH+4. It is formed by the protonation of ammonia (NH3). Ammonium is also a general name for positively charged or protonated substituted amines and quaternary ammonium cations (NR+4)...Co-:NH3 coordination bonds are due to the donation of the lone pair of electrons on N to the Co3+. so this is equal to the number of moles of NH3 present. The compound [CoCl2(NH3)4] can exist as in two isomeric forms which differ in the arrangement of the ligands in space.Enter an equation of a chemical reaction and click 'Submit' (for example: so32-+cr2o72- -->cr3++so42- ). Rules for typing equations. Spaces are irrelevant, for example Cu SO 4 is equal CuSO4. All types of parentheses are correct, for example K3[Fe(CN)6].
PDF Microsoft Word - CH037ed.doc | (aq)
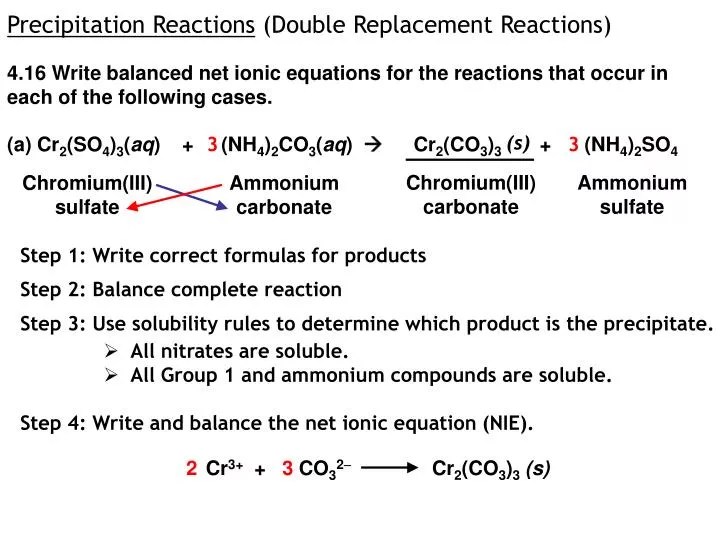
...(aq) + H2O (l) b. Solid chromium(III) hydroxide reacting with nitric acid Cr(OH)3 (s) + 3HNO3 (aq) Cr(NO3)3 (aq) + 3H2O (l) Cr(OH)3 (s) + 3 H+ (aq) (l) oxidation - reduction reaction; Zn is oxidized, N is reduced 6. a. Calculate the molarity of a solution made by dissolving 0.145 mol Na2SO4 in enough...Second, we write the states and break the soluble ionic compounds into their ions (these are the strong electrolytes with an (aq) after them). In this reaction, Cr2(CO3)3 will be insoluble and will be a precipitate (solid) and fall to the bottom of the test tube.Cr2(SO4)3(aq)+(NH4)2CO3(aq)→. The diagrams to the right show the distribution and arrangement of gas particles in two different containers.mol Na2SO4 L of solution. 35. The Ksp of iron(II) hydroxide is 8.0 x 10-16. What is the maximum concentration of Fe2+ ions that can exist in a solution in which [OH1-] = 1.0 x 10-7 M?Terms in this set (6). AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) --> AgCl(s) + KNO3(aq).
You would possibly assume that you'd get a precipitate of chromium(III) carbonate, however this isn't the case.
This is because of the acidic nature of #sf(Cr_((aq))^(3+))#. This is a complex with 6 water ligands surrounding the central steel ion.
Because the #sf(Cr^(3+))# ion is small and highly charged this has the effect of removing electron density from the 0-H bonds, making them weaker. If a base is provide then #sf(H^+)# ions might be misplaced:
#sf([Cr(H_2O)_6]^(3+)+H_2Orightleftharpoons[Cr(H_2O)_5OH]^(2+)+H_3O^(+))#
Many transitional salts are acidic as a result of this. In the presence of a stronger base equivalent to #sf(CO_3^(2-))# then additional protons can also be misplaced:
#sf([Cr(H_2O)_5OH]^(2+)+H_2Orightleftharpoons[Cr(H_2O)_4(OH)_2]^(+)+H_3O^+)#
#sf([Cr(H_2O)_4(OH)_2]^(+)+H_2Orightleftharpoons[Cr(H_2O)_3(OH)_3]+H_3O^+)#
The ultimate species is neutral so is not very water soluble and the substance drops out of solution as a inexperienced, gelatinous precipitate.
The hydrogen ions react with the carbonate ions in an acid/base response:
#sf(2H_3O^(+)+CO_(3)^(2-)rarr3H_2O+CO_2)#
Effervescence is observed due to the formation of #sf(CO_2)#.
Please write a clear answer and easy to read Complete the ...

PPT - Precipitation Reactions (Double Replacement ...

#12 Key

Answered: Write balanced net ionic equations for… | bartleby

CHEM - Towson University - Course Hero

PPT - พันธะเคมี ( Chemical bond) PowerPoint Presentation ...
Answered: Write balanced net ionic equations for… | bartleby

Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that ...
426 Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions ...

PPT - พันธะเคมี ( Chemical bond) PowerPoint Presentation ...

PPT - Precipitation Reactions (Double Replacement ...
write a balanced netbipnic equation for the reaction NiBr2 ...

Key

Solved: Write Balanced Net Ionic Equations For The Reactio ...

PPT - พันธะเคมี ( Chemical bond) PowerPoint Presentation ...

Chemistry Archive | February 27, 2017 | Chegg.com
Write balanced net ionic equations for the reactions that ...

0 comments:
Post a Comment