Textile manufacturing or production is a very complex process. The range of textile. The object of textile finishing is to render textile goods fit for their purpose or end- use and/or improve serviceability of the fabric. The sequence of the rollers is that no two hard rollers are in contact with each other.The event that best describes the role of textile manufacturing in initiating industrialization is as follow. The advancement of the textile industry started with the manufacturing of cotton products or we can say that the establishment of cotton industries.The manufacturing is a crucial part of any clothing business, no matter the size, so spend time finding, speaking to To start a textile business from scratch, you may need possibly $100 at minimum. But which part of the textile industry do you wish to join? If you intend to start a clothing business, the...Behaviour of the employee, stress levels of the employee, working hours, salary and materials handled by the employee best describes the industry that one works. Working industry of an individual can be best described by many factors like different sectors employees behave differently and salaries of...Identify and describe an organization's value proposition. This chapter will emphasize the role of marketing in business, but many of the concepts will apply to non-profit organizations, advocacy campaigns, and other activities aimed at influencing perceptions and behavior.
Which sequence of events best describes the role of textile...
The statement describes a business's revenue and expenses over a period of time. 52. The area of accounting that serves the decision-making needs It is essential to help make business decisions. 54. The accounting assumption related to expressing transactions and events in monetary unit is called...Studies in event perception have shown that people impose boundaries onto the constant flux of perceptual information and perceive the world to be composed of a series of discrete events. Lu, S., Wakefield, L., Faulkenberry, T.: The role of beginnings, ends, and overlap in event representations.What guidelines regarding #isic1392 - Manufacture of made-up textile articles, except apparel can be formulated for the roles involved? These may include best practices, standards, success stories, guidelines, studies, books, databases, forums,… The intended outcomes of the activity are described...Marketing primarily involves the process of creating, promoting and delivering the goods and services to consumers. The primary P's of marketing are: Product, Price, Place, Promotion/Distribution and People. The article Marketing Fundamentals Quiz provides Important Marketing Aptitude multiple...

What is the cost to start a big textile industry? - Quora
Елизавета, role models.Competing among leading global textile producers, Thailand's textile industry has developed significantly over the past five decades. Thailand is one of the few countries in the world that provides the whole value chain of the textile industry, from upstream, midstream, to downstream.Which sequence of events best describes the role of textile manufacturing in initiating industrialization? A. India demanded more cotton textiles, inventors created weaving machines, and factories housed those machines. B. Demand for cotton grew and the textile industry was...Which of the following terms would a marketer use to describe a specific mix of human traits that may be attributed to a particular brand? A marketing research company asked members of a focus group to describe several motorcycle brands as animals.Describe entrepreneurial functions of an entrepreneur. What is the need of entrepreneurship in an economy? Mehak wants to start a textile unit near Gurgaon. In recent decades the role of an entrepreneur has been considered of very great significance in accelerating the pace of growth and...
Home Take Quiz
1. __________ refers to the process of rising interdependence among resource supplies, product markets, and business pageant on a worldwide basis.A. GlobalisationB. International managementC. The multinational economyD. Global managementE. Transnational interdependence
A. Globalisation
2. Which of the following does NOT describe the traits of international managers?A. Focusing on home market demandsB. Being competent in running with persons from other culturesC. Being knowledgeable about international developmentsD. Being mindful of regional developments in a converting worldE. Being transnational in outlook
A. Focusing on home market demands
3. Which of the following correctly describes member countries of the forum for Asian-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC)?A. The member international locations constitute 3 quarters of the international market.B. The member countries represent one 3rd of the global's top market for vehicles and telecommunications apparatus.C. The member nations supply each high price labour and a rising pool of extremely professional brainpower.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
B. The member nations constitute one 3rd of the international's best marketplace for automobiles and telecommunications equipment.
4. The Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) supplies for Asia-Pacific economies to reinforce regional links andA. give a contribution to Australia's securityB. deepen financial relationships with ChinaC. pursue commonplace trade and financial goalsD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
C. pursue commonplace trade and economic targets
5. The Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) facilitates a developed-country forum in which Australia and New Zealand can meet with _______ to talk about economic, business and social policy concerns.A. Japan, North America and Western EuropeB. Pacific Rim countriesC. Canada, US and MexicoD. Japan, Indonesia and ChinaE. North America and Britain
A. Japan, North America and Western Europe
6. Australia's strengthening cooperation with Asia contributes toA. Australia's securityB. promotion of global interestsC. greater industry collaborationD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
7. Which of the following statements about the dating between Australia and New Zealand is right?A. The Trans-Tasman Mutual Recognition Arrangement used to be disbanded in 2002.B. The gap between Australia and New Zealand's business legislation regimes is widening.C. There is a rise in compliance costs for companies working in both international locations.D. The courting between the two international locations stays strong, and is clear from the development on the development on the proceeding Trans-Tasman trade and financial agenda.E. The dating between Australia and New Zealand is weakening economically.
D. The dating between the two countries stays strong, and is obvious from the progress on the growth on the proceeding Trans-Tasman business and economic time table.
8. Which of the following are aggressive implications for the European Union?A. Free glide of staff, goods and services, and investments throughout nationwide boundariesB. Each EU nation has get right of entry to to a marketplace fairly smaller than the United States.C. Unfavourable business and customs lawsD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
A. Free drift of workers, goods and services, and investments throughout nationwide boundaries
9. The European Union is composed of 27 Western European nations that haveA. made up our minds to promote cultural exchanges.B. shaped a political alliance to overthrow communism.C. signed a mutual defence treaty.D. agreed to promote mutual financial enlargement via disposing of trade boundaries.E. created an international organisation to represent the rights and pursuits of employees.
D. agreed to advertise mutual economic expansion through putting off trade barriers.
10. The __________ is/are comprised of 27 international locations related in combination through favourable business and customs rules to facilitate the free flow of employees, merchandise and investments across national barriers.A. European free industry organisationsB. European countriesC. European UnionD. European International AssociationE. European overseas nations
C. European Union
11. Important trade and financial agreements amongst the EU countries include all the following EXCEPTA. discouraging a common foreign money amongst members.B. opening govt procurement to businesses from all member international locations.C. growing uniform minimal technical product standards.D. unifying monetary regulations.E. getting rid of frontier controls and industry boundaries.
A. discouraging a commonplace forex amongst participants.
12. The __________ is the new common foreign money of the European Union.A. Gold StandardB. ZlotyC. EuroD. EU Franc-MarkE. International Dollar
C. Euro
13. Which of the following is NOT an expected receive advantages of a commonplace European currency?A. A not unusual forex will help create steady growth.B. A not unusual currency may have political dangers.C. A commonplace currency will do away with economic risks.D. A common currency will produce lower inflation charges.E. A commonplace currency will give a contribution to raised productivity.
C. A commonplace foreign money will do away with economic dangers.
14. Countries that experience joined in combination to shape the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) includeA. Canada, the United States and MexicoB. Canada, Cuba and MexicoC. Canada and MexicoD. Mexico and the United StatesE. Canada and the United States
A. Canada, the United States and Mexico
15. One of the controversies related to NAFTA is the operation of manufacturing plants which might be allowed to import fabrics, components and gear accountability unfastened. These corporations are calledA. privileged.B. unfastened business organisations.C. Canamericos.D. government agencies.E. Maquiladoras.
E. Maquiladoras.
16. The North American Free Trade Agreement has created a marketplace of potential consumers better than its rival, theA. European Foreign Countries.B. European Union.C. European Free Trade Organisation.D. European International Association.E. North American and European Association.
B. European Union.
17. Which one of the following statements does NOT appropriately describe the concerns of the countries that negotiated the North American Free Trade Agreement?A. American politicians were fascinated with the attainable loss of jobs to Mexico.B. Mexico feared an additional intrusion of US culture and values into Mexico.C. Canadians worried about a limiteless inflow of Mexican immigrants into Canada, thereby offering a cheap source of labour.D. Americans complained that Mexican companies had decrease social requirements relating to the use of kid labour and coverage of the surroundings.E. Canadian firms apprehensive about domination by United States producers.
C. Canadians anxious about a vast inflow of Mexican immigrants into Canada, thereby offering an inexpensive supply of labour.
18. Trade between the Canada, Mexico and United States is characterized byA. restricted go with the flow of items and services and products, employees and investments.B. limited glide of items and services and products, workers and investments.C. formulation of overseas financial controls.D. construction of competitive banking boundaries.E. loose glide of items and products and services, workers and investments.
E. loose drift of items and products and services, workers and investments.
19. Along with the EU, __________ is amongst Australia and New Zealand's largest buying and selling partners and assets of overseas funding.A. CanadaB. USAC. MexicoD. All of the above.E. None of the above.
B. USA
20. Australia and New Zealand's interest in top quality US engagement in the Asia-Pacific area continues, especially the importance of good US members of the family withA. Japan.B. China.C. Indonesia and the Republic of Korea.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
21. Examples of a success collaborations between Australia/NZ and Latin America includeA. a tariff exemption for woolB. access for cereals and meatC. provide of coal to Mexico's power industryD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
22. Two Harvard University professors' analysis of the foreign funding setting in Africa concluded thatA. Africa's contextual problems are manageableB. Africa's contextual problems must be seen as opportunitiesC. Africa presents a promising marketplace if an organization has the necessary managerial and organisational capabilities to take care of Africa's distinctive trade challengesD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
23. __________ is a region of ethnic turmoil and civil strife in countries struggling along the road to peace and financial development while simultaneously being a area wealthy with global trade opportunities.A. Australia and New ZealandB. North AmericaC. Western EuropeD. Northern EuropeE. Africa
E. Africa
24. Africa is a continent with a growing financial system that beckons global trade because of itsA. natural resourcesB. ethnic turmoilC. risky economic developmentD. All of the above.E. None of the above.
A. natural sources
25. __________ has a tendency to deter international industry in portions of Africa.A. A low economic expansion price in sub-Saharan AfricaB. PovertyC. A continuing AIDS epidemicD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
26. __________ hyperlinks 14 countries of southern Africa in business and economic development efforts.A. South African Free Trade Association (SAFTA)B. South African Community (SAC)C. South Africa Economic Cooperative (SAEC)D. South African Development Community (SADC)E. South Africa Union (SAU)
D. South African Development Community (SADC)
27. Businesses enlarge their operations to the world marketplace for lots of causes. Which of those is NOT a reason why presented by way of your text?A. To have access to decrease labour costsB. To draw on the monetary sources of many nationsC. To take benefit of lowered governmental keep watch over in host countriesD. To build up get entry to to wanted uncooked materialsE. To extend profit doable
C. To take advantage of diminished governmental keep an eye on in host international locations
28. Conducting for-profit transactions of items and services and products across national boundaries is the basis ofA. multinational managementB. transborder entrepreneurshipC. cross-cultural intrapreneurshipD. global businessE. cross-national management
D. international industry
29. The reasons for engaging in global business come with all of the following EXCEPTA. looking for new markets to promote products.B. seeking profit doable.C. searching for to eliminate moral issues.D. in search of get right of entry to to financial sources.E. searching for get entry to to lower labour costs.
C. searching for to do away with ethical considerations.
30. A free-market economy is one thatA. lets in the executive to determine allocations of raw fabrics.B. operates beneath capitalism and rules of supply and insist.C. allows the govt to make all the primary choices.D. disperses nationwide assets equitably amongst the firms in the country.E. disperses nationwide assets equally among the citizens of a nation.
B. operates under capitalism and regulations of provide and insist.
31. When the government makes decisions that decide allocations of raw materials, set product output quotas, and keep an eye on wages and costs, the nation is operating underA. prerequisites of loose government control.B. a central-planning financial system.C. deficient executive stipulations.D. a home financial system.E. a free-market economy.
B. a central-planning economy.
32. Controversies emerge over rising prices, unemployment, trade competition and the challenges of privatisation asA. world markets dominate transnational businessesB. as manufacturing-based economies change to knowledge-based economiesC. a free-market economies trade to central-planning economiesD. as central-planning economies trade to free-market economiesE. globalisation increases aggressive pressures on companies of all sizes
D. as central-planning economies trade to free-market economies
33. The collapse of communism in the former Soviet Union and the international locations ruled via itA. will provide dangers to overseas investors because of adjustments in political systems and governmentsB. will provide opportunities to foreign traders in Russia, and eastern and central EuropeC. have produced an atmosphere of social progress and economic enlargement, thereby developing opportunities for western businessesD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
34. __________ is the promoting of state-owned enterprises into personal possession.A. Governmental subsidyB. Foreign investmentC. PrivatisationD. Governmental auctionE. Corporate welfare
C. Privatisation
35. Political requires tariffs and beneficial remedy to assist refuge domestic businesses from foreign pageant is known asA. restrictive industry.B. protectionism.C. maquiladora.D. free trade.E. strategic financial bidding.
B. protectionism.
36. Common legal problems in global business involve all of the following EXCEPTA. incorporation practices and business ownership.B. protecting patents, logos, and copyrights.C. handling foreign currency echange restrictions.D. environmental pollution restrictions.E. negotiating and imposing contracts with international events.
D. environmental air pollution restrictions.
37. Foreign firms working in the Asia-PacificA. may come across moderately other laws than they're aware of in their home countries.B. will have to handle antitrust problems that prevent competitors from regularly speaking with one some other.C. should take care of particular laws referring to occupational protection and well being, equal employment alternative and sexual harassment.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
38. Because tutorial techniques range from country to country, industry leaders around the global are involved aboutA. precise or potential human resource deficits.B. issues of illiteracy.C. the absence of appropriate abilities in the personnel.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
39. Which of the following does NOT appropriately characterise the habits of global trade?A. Joint ventures and wholly owned subsidiaries are direct funding strategies for engaging in world trade.B. Direct investment strategies require primary capital commitments but create rights of possession and keep watch over over foreign operations.C. Market access strategies involve the sale of items or services and products to foreign markets however don't require main capital investments.D. When a business is solely getting started the world over, direct funding methods are the usual solution to begin.E. Global sourcing, exporting/importing and licensing/franchising are marketplace entry strategies for accomplishing international trade.
D. When a trade is solely getting began internationally, direct investment strategies are the usual way to begin.
40. ____________ supplies a industry with the alternative to take merit of world wage gaps and the availability of skilled labour by means of dispersing increasingly more work to overseas locations.A. Direct investmentB. LicensingC. ExportingD. Global sourcingE. Importing
D. Global sourcing
41. The exporting of merchandise involvesA. acquiring foreign-made products and promoting them in home markets.B. selling in the community made products in foreign markets.C. contracting to supply managerial and technical carrier to a international worry.D. making direct investments in start-up operations out of the country.E. making investments in a foreign operation.
B. promoting locally made merchandise in international markets.
42. The uploading of merchandise involvesA. acquiring foreign-made merchandise and promoting them in domestic markets.B. contracting to supply managerial and technical provider to a international fear.C. making investments in a overseas operation.D. selling locally made products in international markets.E. making direct investments in start-up operations abroad.
A. obtaining foreign-made products and selling them in domestic markets.
43. __________ is a form of world trade through which an organization can pay a rate for the rights to fabricate or sell every other company's products.A. A management contractB. An incorporated businessC. A licensing agreementD. A joint ventureE. A multi-company operation
C. A licensing settlement
44. A __________ is a global industry method that usually grants get entry to to unique manufacturing era, a unique patent, or trademark rights.A. control contract.B. licensing settlement.C. wholly-owned subsidiary.D. three way partnership.E. franchise.
B. licensing agreement.
45. A sort of licensing in which the licensee buys the whole improve package had to open the business is aA. franchiseB. wholly-owned subsidiaryC. joint ventureD. control contractE. licensing agreement
A. franchise
46. Joint ventures are __________ that lend a hand participants to gain things thru cooperation that otherwise can be tough to reach independently.A. strategic alliancesB. licensing agreementsC. management contractsD. import/export arrangementsE. international partnering contracts
A. strategic alliances
47. A checklist for settling on three way partnership partners in another country must include which of the following?A. Choose a overseas spouse with actions that relate intently in your firm's primary industry.B. Choose a foreign partner with a powerful local staff.C. Choose a overseas spouse with good profit attainable and sound monetary standing.D. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
48. In deciding on three way partnership companions abroad, an organization will have to do all of the following EXCEPTA. select a partner that is a new entrant for your company's line of industry.B. make a choice a partner with just right profit potential.C. select a partner with shared pursuits in meeting buyer wishes.D. select a spouse with future expansion probabilities.E. make a selection a partner with a strong local market for its own merchandise.
A. make a selection a spouse that may be a new entrant for your company's line of business.
49. Which of the following paperwork of global business transactions constitute investments in an area operation that is completely owned and regulated through a international firm?A. Management contractsB. Licensing agreementsC. Wholly owned subsidiariesD. A multinational corporationE. Joint ventures
C. Wholly owned subsidiaries
50. The best definition of a multinational corporation isA. a industry that has in depth international operations in multiple international nation.B. a trade company that has intensive operations in one foreign country.C. any joint venture with a overseas company.D. any import/export company.E. any firm that does trade in another country.
A. a industry that has intensive global operations in multiple foreign country.
51. Which of the following are mutual advantages for a multinational company and a bunch country?A. GrowthB. IncomeC. LearningD. All of the aboveE. None of the above
D. All of the above
52. A company that operates worldwide without being recognized with one nationwide house is known as a ___________.A. antidomestic corporationB. world corporationC. supernational corporationD. multinational corporationE. transnational corporation
E. transnational corporation
53. All of the following are advantages to the host country of a multinational company EXCEPTA. reduced tax base.B. greater employment opportunities.C. generation transfer.D. capital development.E. development of native assets.
A. decreased tax base.
54. Multinational companies have a number of proceedings about host international locations. Which of the following is NOT one of these proceedings?A. Pressure to stay local wage rates lowB. Pressure to pay high costs for servicesC. Pressure to shop for raw materials at inflated pricesD. Failure to uphold contractsE. Foreign change restrictions
A. Pressure to stay local wage rates low
55. Multinational corporations are regularly criticised at house forA. diverting labour-intensive jobs from the domestic labour drive to foreign labour markets.B. diverting capital investments away from the domestic market.C. permitting or encouraging corrupt practices in their international subsidiaries.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
56. Which of the following statements about corruption is NOT true?A. Companies adhering to anti-corruption insurance policies are at a aggressive advantage.B. Commonwealth heads of govt have a policy of 'zero tolerance' of corruptionC. The Council of Europe and the EU have finalised comprehensive anti-corruption insurance policies.D. Corruption involves illegal practices to further one's industry practices.E. Critics consider that anti-corruption insurance policies fail to recognise the reality of trade in international international locations.
A. Companies adhering to anti-corruption insurance policies are at a competitive benefit.
57. The extent of world environmental coverage is affected by all of the following considerations and practices EXCEPTA. handiest the highly industrialised international locations are apprehensive about industrial pollution of towns, hazardous waste disposal, and depletion of herbal resources.B. the world's citizenry is concerned about the chances of global environmental screw ups.C. the world's citizenry increasingly more expects world corporations to admire the natural surroundings and to pursue protected commercial practices.D. activist teams are promoting sustainable building to meet the wishes of the present without compromising the talent of long term generations to fulfill their very own wishes.E. ISO 14000 provides pointers for responsible environmental policies.
A. handiest the extremely industrialised nations are anxious about industrial pollution of cities, hazardous waste disposal, and depletion of natural resources.
58. A shared set of ideals, values and patterns of behaviour not unusual to a bunch of other people is referred to asA. national style.B. team personality.C. the economic gadget.D. tradition.E. the legal machine.
D. tradition.
59. __________ is the confusion and discomfort an individual reports when in an unfamiliar culture.A. Culture shockB. EthnocentrismC. PolycentrismD. GroupthinkE. Jet lag
A. Culture surprise
60. Which sequence accurately describes the stages that a person goes via in adjusting to a new tradition?A. Confusion, inflammation/anger, reality, small victories and the honeymoonB. The honeymoon, small victories, truth, confusion and irritation/angerC. Small victories, the honeymoon, fact, irritation/anger and confusionD. Confusion, small victories, the honeymoon, irritation/anger and realityE. The honeymoon, confusion, inflammation/anger, small victories and reality
D. Confusion, small victories, the honeymoon, irritation/anger and truth
61. __________ cultures are those in which much conversation takes position through nonverbal and situational cues along with the written or spoken phrase.A. High-contextB. Low-context.C. OrganisationalD. CorporateE. Middle-context
A. High-context
62. Which of the following statements supplies an flawed description of the role of interpersonal space in tradition?A. Arabs favor nearer interpersonal area in terms of communique.B. Americans tend to value massive and private workplace space.C. Interpersonal space is a silent language of culture.D. Australians and New Zealanders want shut interpersonal area in interpersonal communications.E. In Japan, executive workplaces usually are shared even in main companies.
D. Australians and New Zealanders choose shut interpersonal area in interpersonal communications.
63. In __________, folks have a tendency to do something at a time.A. moral culturesB. monochronic culturesC. time dependent culturesD. polychronic culturesE. delicate cultures
B. monochronic cultures
64. In __________, time is used to accomplish many things directly.A. monochronic culturesB. time dependent culturesC. sensitive culturesD. polychronic culturesE. ethical cultures
D. polychronic cultures
65. As a cultural variable, religion mayA. affect business practices relating to dress, meals and interpersonal behaviour.B. supply moral and ethical steering for personal and institutional activities.C. require business people to be delicate to the rituals, holy days, and different expectancies associated with the host nation's spiritual tradition(s).D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
66. Which of the following is a real statement about the role of contracts in numerous cultures?A. Cultures range of their use of contracts and agreements.B. In China a contract is considered as a final and binding settlement.C. In low-context cultures, written contracts continue to emerge and are changed as the parties paintings together.D. Written contracts are viewed as a place to begin in low-context cultures.E. Contracts tend to be considered as binding agreements in high-context cultures.
A. Cultures range of their use of contracts and agreements.
67. Geert Hofstede has advanced a framework consisting of 5 dimensions for understanding the control implications of wide differences in national cultures. Which of the following appropriately identifies those 5 dimensions?A. Location, simple task avoidance, individualism-collectivism, masculinity-femininity and spiritual traditionB. Power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism-collectivism, masculinity-femininity and time orientationC. Power distance, simple task avoidance, individualism-utilitarianism, masculinity-femininity and religious traditionD. Political distance, uncertainty avoidance, utilitarianism-collectivism, masculinity-femininity and time orientationE. Power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism-collectivism, totalitarianism-decentralisation and financial opportunities
B. Power distance, uncertainty avoidance, individualism-collectivism, masculinity-femininity and time orientation
68. Which of the following examples represent Hofstede's individualism-collectivism measurement?A. All should have equivalent rights as opposed to best the ones in keep an eye on are entitled to privilegeB. Willingness to take dangers versus fear with safety in lifeC. Reliance on person self-interest as opposed to the collective values of the groupD. Interdependence versus independenceE. Time is unfastened versus time is cash
C. Reliance on particular person self-interest as opposed to the collective values of the staff
69. Which of the following examples represent Hofstede's masculinity-femininity measurement?A. Willingness to take dangers as opposed to concern with safety in lifeB. Everyone will have to have equivalent rights versus handiest the ones in keep an eye on entitled to privilegeC. Time is unfastened versus time is cash.D. Reliance on group choices versus reliance on particular person decisionsE. Assertiveness as opposed to concerns for emotions
E. Assertiveness as opposed to considerations for feelings
70. Which of the following examples represent Hofstede's energy distance size?A. Everybody should have equal rights as opposed to the ones who are in keep an eye on are entitled to privilege.B. Willingness to take dangers as opposed to worry with security in life.C. Interdependence versus independence.D. Reliance on staff selections versus reliance on person selections.E. Time is unfastened versus time is money.
A. Everybody should have equal rights as opposed to the ones who are in keep an eye on are entitled to privilege.
71. Hofstede's cultural framework helps determine helpful managerial implications of cultural variations, including all of the following EXCEPTA. in high uncertainty avoidance cultures, employment practices that increase task safety are most likely to be used.B. staff from high energy distance cultures can be expected to respect folks in authority.C. in highly individualistic societies, workers are prone to emphasise self-interests over team loyalty.D. in long-term cultures, business methods are oriented toward the longer term.E. in more feminine societies, the place of job displays extra inflexible gender stereotypes.
E. in additional female societies, the office shows extra rigid gender stereotypes.
72. Fons Trompenaars' framework for identifying systematic cultural variations focuses onA. the approach relationships are treated amongst folks.B. attitudes toward time.C. attitudes toward the environment.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
73. According to Fons Trompenaars, __________ is the stage to which a tradition emphasises individual freedoms and tasks in relationships or focuses more on staff interests and openness.A. success versus prescriptionB. universalism as opposed to particularismC. specific versus diffuseD. impartial as opposed to affectiveE. individualism as opposed to collectivism
E. individualism versus collectivism
74. According to Fons Trompenaars, __________ is the degree to which a culture emphasises objectivity and reserved detachment in relationships or allows for extra emotionality and expressed feelings.A. fulfillment as opposed to prescriptionB. particular versus diffuseC. universalism as opposed to particularismD. impartial versus affectiveE. individualism as opposed to collectivism
D. impartial as opposed to affective
75. According to Fons Trompenaars, __________ is the stage to which a tradition emphasises focused and in-depth relationships or broader and more superficial ones.A. individualism versus collectivism.B. neutral as opposed to affective.C. specific as opposed to diffuse.D. achievement versus prescription.E. universalism versus particularism.
C. specific versus diffuse.
76. According to Fons Trompenaars, __________ is the stage to which a culture emphasises regulations and consistency in relationships or accepts flexibility and the bending of regulations to fit circumstances.A. universalism as opposed to particularismB. individualism versus collectivismC. impartial versus affectiveD. explicit as opposed to diffuseE. achievement versus prescription
A. universalism as opposed to particularism
77. The __________ refers to a tradition that views time as a continuous and passing collection of events.A. synchronic viewB. polychronic viewC. time sense of right and wrong viewD. sequential viewE. appreciation for time view
D. sequential view
78. The __________ refers to a tradition that perspectives time as linear with an interrelated previous, provide and long run.A. Time conscience viewB. Polychronic viewC. Analytical view of timeD. Synchronic viewE. Sequential view
D. Synchronic view
79. Trompenaars recognises that cultures vary of their technique to the surroundings. In a(n) __________ tradition, folks tend to view themselves as break away nature.A. outer-directedB. self-motivatingC. self-directedD. inner-directedE. distrusting
D. inner-directed
80. Fons Trompenaars' cultural framework suggests that in a(n) __________ tradition, folks tend to view themselves as phase of nature.A. humanistB. inner-directedC. naturalistD. outer-directedE. environmentally friendly
D. outer-directed
81. The world supervisor is a person who isA. ok with cultural diversity.B. quick to find opportunities in unfamiliar settings.C. able to utilise financial, social, technological, and different forces for the benefit of the organisation.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
82. __________ is the learn about of how management practices systematically vary amongst nations and/or cultures.A. Political-risk analysisB. International businessC. Comparative managementD. International managementE. Theory Z
C. Comparative management
83. Which one of the following is NOT true referring to planning and controlling of global operations?A. Global making plans and controlling don't seem to be especially challenging or tough because of the availability of computer-based world networks.B. Businesses with investments in international countries must stay wary about the menace of doing industry across political and financial borders.C. Political menace research is used to forecast the likelihood that events - like social instabilities dues to ethnic differences, armed conflicts, and new regulations and financial policies -- will threaten the security of a international funding.D. The house administrative center will have to be linked with foreign associates whilst bearing in mind other environments, cultures and needs.E. Increasingly, technology facilitates the making plans and keep watch over of global communications through massively progressed communications methods.
A. Global making plans and controlling don't seem to be particularly difficult or difficult because of the availability of computer-based global networks.
84. __________ is the attainable loss of one's investment in or managerial control of a foreign asset because of changes in the host nation's political atmosphere.A. Political riskB. Corporate malfeasanceC. Political instabilityD. Economic instabilityE. Sociocultural threat
A. Political menace
85. Forecasting the likelihood of events that can threaten the safety of a foreign investment is referred to as __________ analysis.A. foreign-instabilityB. securityC. economic-securityD. political-riskE. investment-risk
D. political-risk
86. __________ refers to doable loss because of fluctuating exchange charges.A. Social riskB. Economic riskC. Currency riskD. Political riskE. Business threat
C. Currency threat
87. The private attributes that are thought to be essential for workers accepting in a foreign country assignments come with all of the following EXCEPTA. an actual need to reside and work in a foreign country.B. circle of relatives flexibility and support.C. a excessive stage of normal cultural awareness.D. technical competence in one's jobE. a powerful sense of non-public ethics.
E. a strong sense of private ethics.
88. One of the concerns of multinational firms is whether or not accepted US and Western European management practices and theories are suitable to be used as fashions abroad. Hofstede's analysis on this house indicates that those theoriesA. work best within multinational companies.B. paintings best inside of English-speaking nations.C. are nonetheless ethnocentric.D. are simplest legitimate within the country they have been created in.E. are universally appropriate since they are good theories.
A. work best inside multinational corporations.
89. The textual content discusses characteristics of the Japanese way to control. Which of the following is NOT one of these characteristics?A. Japanese staff intend to work for an organisation their entire profession.B. Japanese managers like to make group selections.C. Japanese companies emphasise high quality.D. Japanese managers experience gradual occupation advancement.E. Japanese follow emphasises task enrichment, specializing in restructuring particular person jobs to suit person needs.
E. Japanese apply emphasises activity enrichment, that specialize in restructuring individual jobs to suit individual wishes.
90. In Japan, __________ are long-term business alliances or industry groups that link in combination quite a lot of companies -- producers, providers and finance firms -- to attain not unusual pursuits.A. sushiB. jujitsuC. kanbanD. keiretsuE. Yokohama
D. keiretsu
91. Companies that believe in __________, realise that businesses round the world have a lot to percentage with and be told from on any other.A. world tradeB. cross-cultural control of intellectual propertyC. expatriate data sharingD. world organisational learningE. transnational knowledge positioning
D. world organisational learning
92. To advertise global organisational finding out, organisations and their individuals shouldA. percentage with and be told from one another, specifically from excellent corporations, each at home and out of the country.B. admire the constraints and alternatives of different national cultures and environments.C. be alert, open, inquiring, and wary relating to the potential merits of control practices present in other countries and the way they are affected by cultural variables.D. All of the above.E. None of the above.
D. All of the above.
米兜彩票官网Feed | Tractica

Louis Daguerre - Who is talking about Louis Daguerre on ...

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Europe - ThinEbook E-books

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Example Of Business Proposal Letter | Apparel Dream Inc

Europe - ThinEbook E-books

Small Business Answers - How many stamps do I need to send ...

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Louis Daguerre - Who is talking about Louis Daguerre on ...

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

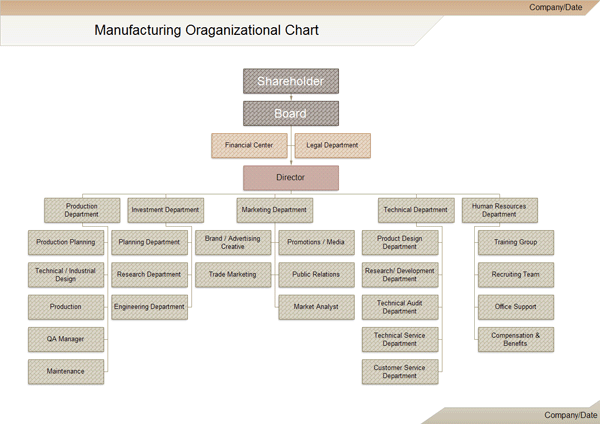
Example of Organizational Chart
Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Русский АвтоМотоКлуб | Экспресс-помощь на дорогах для ...

Multiple Choice Questions 1-17 - 04-71-243: Human ...

Europe - ThinEbook E-books

26 best Photosynthesis and Cell Respiration images on ...

Strat Matters | Exploring how planning and managing ...

Small Business Answers - Best stay at home job?I have 3 ...

Europe - ThinEbook E-books

0 comments:
Post a Comment